Giant Hole the Size of 60 Earths Emerges on Sun, Spewing Solar Wind.
Others are reading now
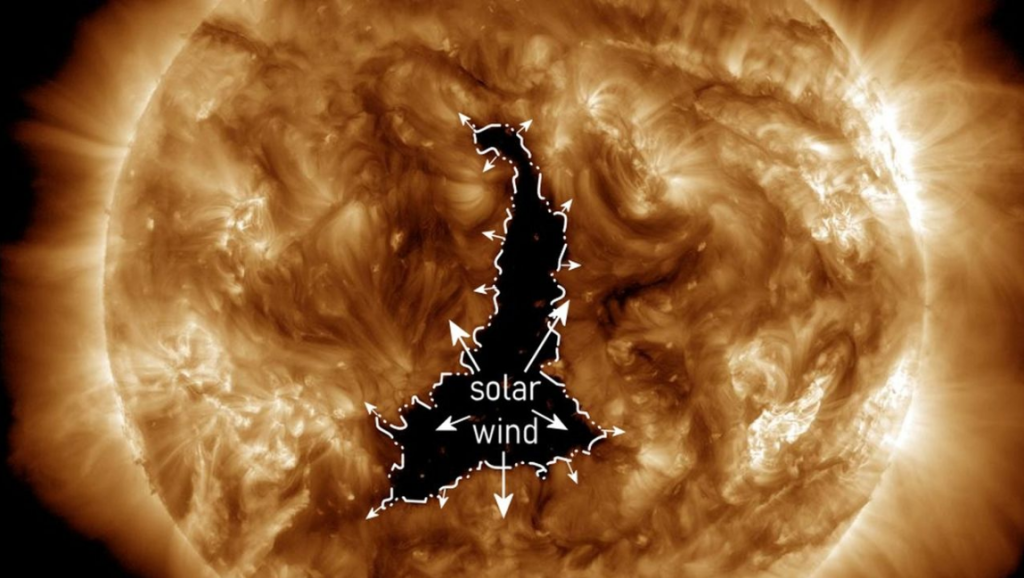
A massive coronal hole, spanning a width greater than 60 Earths, has recently formed near the sun’s equator, marking an unusual occurrence in the current solar cycle.
According to Kompas.id, this vast and dark gap on the sun’s surface, identified as a coronal hole, has been emitting high-speed solar wind streams directly towards Earth.
The phenomenon was first observed on December 2, when the hole rapidly expanded to an impressive width of approximately 497,000 miles within a day, as reported by Spaceweather.com.
The appearance of this coronal hole, particularly its size and location near the sun’s equator, is intriguing to scientists, as it deviates from the typical patterns observed during the solar cycle.
Also read
Coronal holes are known to be cooler and less dense regions on the sun, appearing darker compared to the surrounding areas. They are formed due to the opening of the sun’s magnetic fields, allowing solar wind to escape.
These regions are usually visible in ultraviolet light and are more common during the solar minimum phase.
Despite initial predictions of a moderate geomagnetic storm resulting from this solar event, the impact on Earth has been milder than expected.
The solar wind has been less intense, leading to a weaker geomagnetic storm. However, the possibility of auroras, particularly at higher latitudes, remains.
The duration of this coronal hole’s presence is uncertain, though it could last beyond a single solar rotation, which is about 27 days.
This recent solar activity, including the emergence of this colossal coronal hole, adds to a series of notable events observed in the sun this year.
These include a “sunspot archipelago,” a dramatic “canyon of fire” eruption, and a potent solar flare. Such activities suggest that the sun is approaching its solar maximum, the peak of the 11-year solar cycle. Scientists now predict the onset of the solar maximum to occur in early 2024, revising their earlier forecasts.
The emergence of this giant coronal hole challenges existing norms about the solar cycle and highlights the dynamic and unpredictable nature of our closest star. As the sun continues to exhibit unusual behavior, it provides scientists with valuable insights into solar dynamics and its effects on Earth.