When choosing a new phone, it’s not just functionality and design that matter, but also how much electromagnetic radiation the device emits.
Others are reading now
When buying a new phone, most people focus on features and design. But an important factor that is often overlooked is the amount of electromagnetic radiation the device emits.
This radiation, which is absorbed by the human body, is measured by the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) index.
What is the SAR Index?
The SAR value indicates how much electromagnetic radiation is absorbed by the body when using a phone. It is expressed in watts per kilogram (W/kg) or grams (W/gr). The SAR value is especially relevant because phones are used close to the body and head.
The European Union has set guidelines for maximum SAR values to ensure user safety. These guidelines are:
Also read
-
0.08 W/kg for whole-body exposure.
-
2 W/kg for specific body parts, like the head.
These limits are calculated based on an average exposure over 10 grams of tissue during a six-minute period. All phones sold within the EU must meet these standards.
Factors Affecting SAR Values
Several factors can influence the SAR index for phones. One of the key elements is network quality; a stronger signal means your device emits less radiation.
The location of the device in relation to the body also impacts the SAR value. According to the inverse square law, the SAR value can be significantly reduced by increasing the distance between the device and the body.
For example, if a device has a SAR value of 2 W/kg at a distance of 5 cm, the value drops to 0.50 W/kg if the distance is increased to 10 cm.
To minimize radiation exposure, consider using hands-free options or wireless Bluetooth. It’s also important to note that the highest SAR measurement occurs under harsh conditions, meaning actual daily exposure is usually much lower, often less than what lower SAR index devices might suggest.
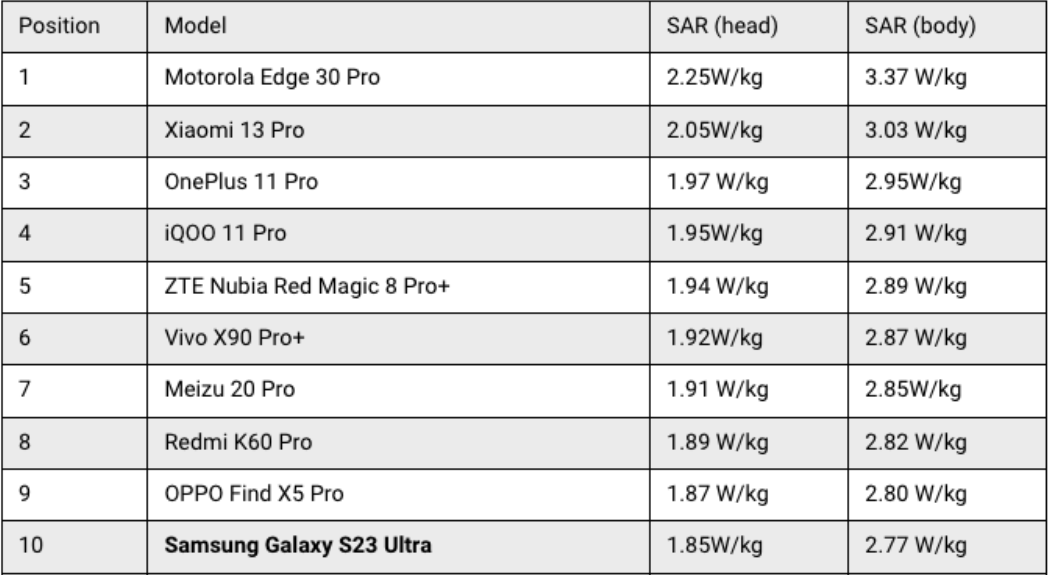
Here are the 10 phones that emit the most SAR radiation:
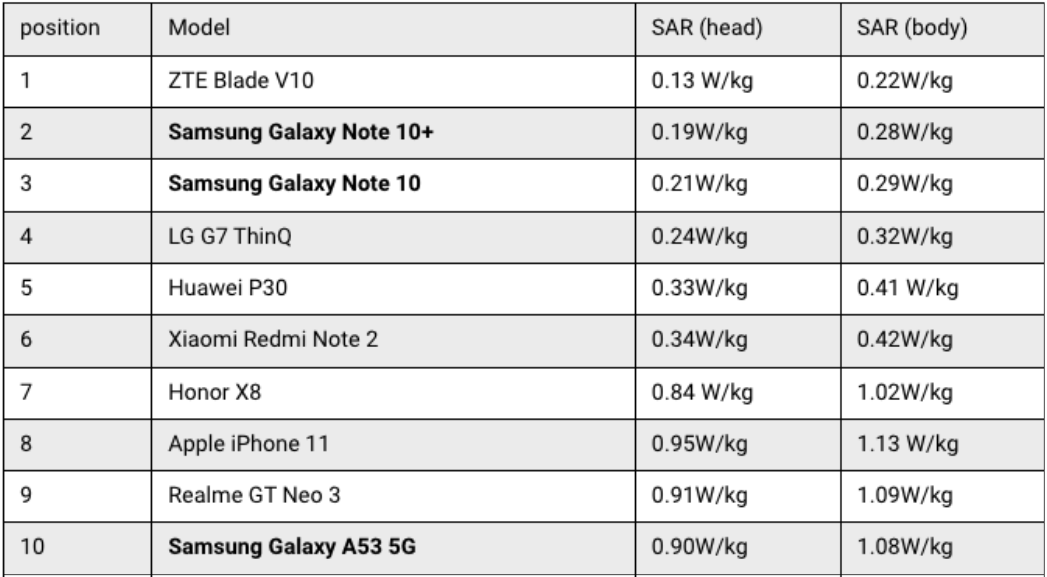
And the 10 phones that emit the least SAR radiation: